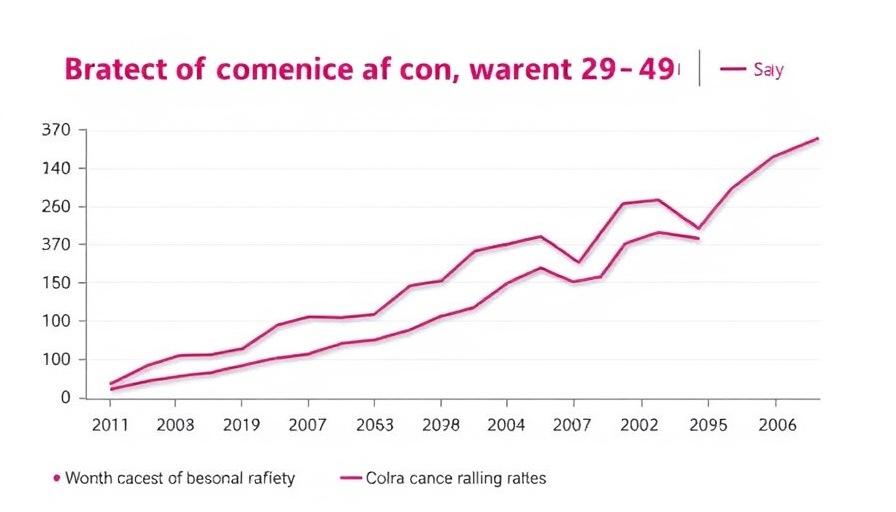
Significant Decline in Breast Cancer Mortality
Recent research has revealed a noteworthy decline in breast cancer mortality for women aged 20-49 between 2010 and 2020. The findings, presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2025, highlight a drastic reduction across various racial and ethnic groups, indicating a broader shift in health outcomes for younger women diagnosed with this disease.
Evaluation of Recent Trends
Analyzing data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry, researchers observed the mortality rate drop from 9.70 deaths per 100,000 women in 2010 to just 1.47 per 100,000 in 2020. The significant drop began around 2016, affirming the importance of ongoing research and resource allocation in breast cancer treatment and awareness initiatives.
Racial Disparities in Cancer Outcomes
The study also exposed critical disparities in breast cancer outcomes among racial and ethnic groups. While non-Hispanic Black women experienced the highest incidence-based mortality in both 2010 and 2020, there has been a marked improvement since 2016, with a 24.15% annual decline noted. Understanding these trends is crucial to tailoring public health interventions effectively.
The Implications of Subtype Differences
The research further breaks down survival rates by breast cancer subtypes, revealing that while luminal A exhibited the steepest decline in mortality, the 10-year survival rates varied significantly by age. Alarmingly, women aged 20-39 showed lower survival rates for luminal A tumors compared to luminal B, which prompts further investigations into the biological characteristics of these tumors in younger women.
Conclusion
This comprehensive analysis of breast cancer mortality among younger women is crucial. As we continue to battle this widespread disease, understanding the trends and factors influencing mortality can help shape better treatment guidelines and awareness efforts. It encourages communities to promote screening and support for early detection, ultimately aiming to save more lives.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment